News
Send Inquiry
A Guide to Procuring 100x150mm Logistics Labels
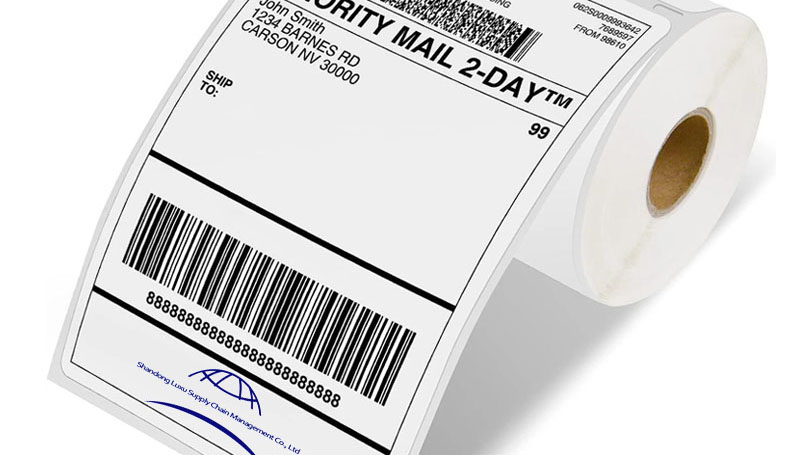
1. Core Components & Specifications
1.1 Face Materials: Selection Criteria
-
Thermal Paper (Direct Thermal):
-
Advantage: Eliminates the need for printer ribbon, offering operational simplicity and cost efficiency for high-volume printing.
-
Consideration: Susceptible to fading over time when exposed to heat, direct sunlight, or chemical abrasion. Ideal for short-term applications such as shipping documents and internal tracking where longevity is not a primary concern.
-
-
Coated Paper (Requires Ribbon):
-
Advantage: Delivers superior print durability, with excellent resistance to smudging and environmental factors. Produces high-contrast, scannable barcodes essential for permanent inventory identification and asset tracking.
-
Consideration: Involves the ongoing cost and handling of printer ribbons.
-
1.2 Adhesive Technologies: Performance & Application
-
Permanent Adhesive (Hot Melt):
-
Profile: Provides high initial tack and strong ultimate adhesion to a variety of corrugated cardboard and shipping box surfaces.
-
Application: The standard choice for general logistics and parcel shipping. Optimal for most warehouse and distribution environments.
-
-
High-Temperature Resistant Adhesive:
-
Profile: Formulated to maintain integrity and prevent oozing or label loss in high-temperature environments, such as during summer transport or in storage facilities without climate control.
-
Application: Critical for supply chains operating in hot climates or for goods subject to temperature fluctuations.
-
1.3 Form Factor: Operational Efficiency
-
Rolls:
-
Best For: Automated application systems, high-speed industrial printers, and environments where space optimization is critical.
-
-
Fanfold (Shelf-Fold):
-
Best For: Manual application settings, desktop printing, and operations requiring frequent label changes. This format minimizes curling and reduces the risk of printer jams.
-
1.4 Standard Packaging: 500 Labels per Pack
A 500-label pack represents an optimal balance for initial procurement, quality testing, and ongoing inventory management. It facilitates efficient stock rotation, minimizes storage footprint, and serves as a practical consumption unit for many small to medium-sized operations.
2. Strategic Procurement Guidelines
To optimize your procurement process, we recommend the following steps:
-
Define Primary Use Case: Determine whether the labels are for short-term shipping documentation (favoring Thermal Paper) or permanent inventory identification (favoring Coated Paper).
-
Assess Environmental Exposure: Evaluate the entire logistics chain for potential exposure to heat, moisture, and abrasion. This assessment is crucial for selecting the correct adhesive and face material combination.
-
Verify Printer Compatibility: Confirm that your printing hardware is configured for either direct thermal or thermal transfer (ribbon-based) technology.
-
Evaluate Operational Workflow: Align the label form factor with your application process. Automated systems typically require rolls, while manual stations benefit from the convenience of fanfold packs.
-
Implement a Quality Assurance Protocol:
-
Request Samples: Prior to bulk ordering, obtain production samples for real-world testing. Key tests should include print quality, barcode scannability, adhesive performance, and durability under expected conditions.
-
Supplier Qualification: Partner with suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality, reliable delivery, and the ability to provide technical data sheets for their products.
-
Initial Order Quantity: Beginning with a 500-label pack per variant is a strategic approach for field validation before committing to larger, more cost-effective volumes.
-

Conclusion
The 100x150mm logistics label is a critical component in a seamless supply chain. A strategic procurement approach, based on a clear understanding of material properties and operational requirements, ensures reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. We recommend a pilot program with shortlisted products to finalize your specification.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français magyar
magyar Malay
Malay Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi عربى
عربى Українська
Українська

